Blazor - Desktop Crossplatform
Getting Started
This tutorial will show you how you can use Smart components in a Blazor Desktop app with .NET 6, running in both a web browser and in WinForms.
Prerequisites
- Visual Studio 2022
- .NET 6 SDK
Before getting started you need to have Visual Studio 2022 with .NET 6 SDK installed.
Blazor Server App
First, we will start by opening Visual Studio 2022 and creating a Blazor Server App called CrossPlatformBlazor with target framework .NET 6.0
Then we need to add Smart.Blazor NuGet package to the project.
Open the \_Imports.razor file and add `@using Smart.Blazor`.
Then open the \Pages\_Layout.cshtml file and include a theme CSS file by adding this snippet:
<link href="_content/Smart.Blazor/css/smart.default.css" rel="stylesheet" />
and Smart source files by adding this snipet:
<script src="_content/Smart.Blazor/js/smart.blazor.js"><script>
<script src="_content/Smart.Blazor/js/smart.elements.js"></script>
The next step is to open the Program.cs file and to add builder.Services.AddSmart(); and using Smart.Blazor; in the using statements.
After that Program.cs file should look like this:
using CrossPlatformBlazor.Data;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Web;
using Smart.Blazor;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddServerSideBlazor();
builder.Services.AddSingleton<WeatherForecastService>();
// Add Smart UI for Blazor.
builder.Services.AddSmart();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.MapBlazorHub();
app.MapFallbackToPage("/_Host");
app.Run();
Now you can open the \Pages\Index.razor file and paste the following code:
@page "/"
@using CrossPlatformBlazor.Data
@inject WeatherForecastService ForecastService
<h1>Weather forecast</h1>
<p>This component demonstrates fetching data from the server.</p>
@if (forecasts == null)
{
<p><em>Loading...</em></p>
}
else
{
<Table Selection="true" SortMode="TableSortMode.One" class="table">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Date</th>
<th>Temp. (C)</th>
<th>Temp. (F)</th>
<th>Summary</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var forecast in forecasts)
{
<tr>
<td>@forecast.Date.ToShortDateString()</td>
<td>@forecast.TemperatureC</td>
<td>@forecast.TemperatureF</td>
<td>@forecast.Summary</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
</Table>
}
@code {
private WeatherForecast[] forecasts;
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
forecasts = await ForecastService.GetForecastAsync(DateTime.Now);
}
}
We are ready with the web part of our application. If you run the project you should see the following result:
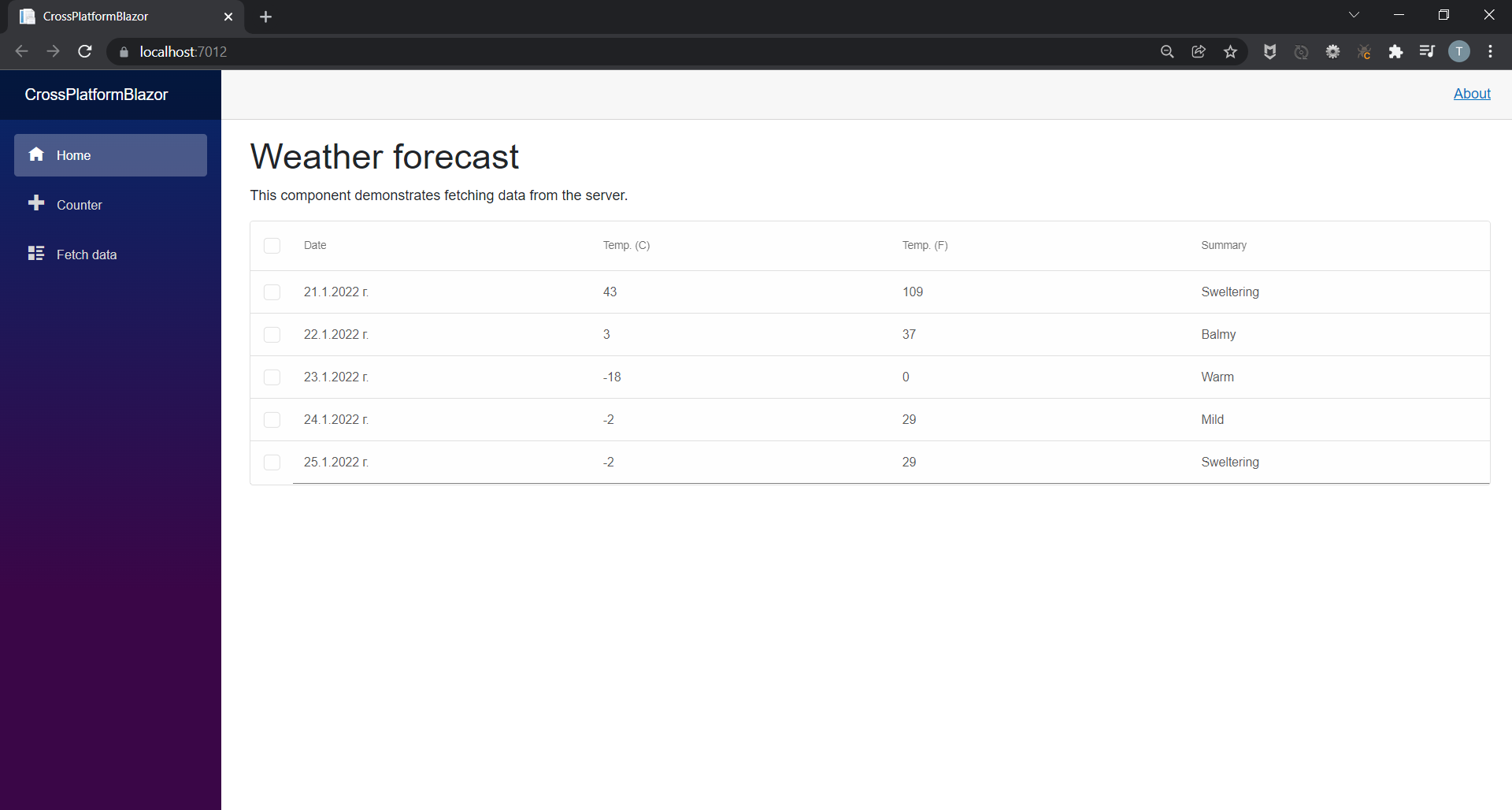
Windows Forms Blazor
The next step is to add a new Windows Forms App to the solution. We will name it WinFormsBlazor.
Add the Smart.Blazor and Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms NuGet packages to the project.
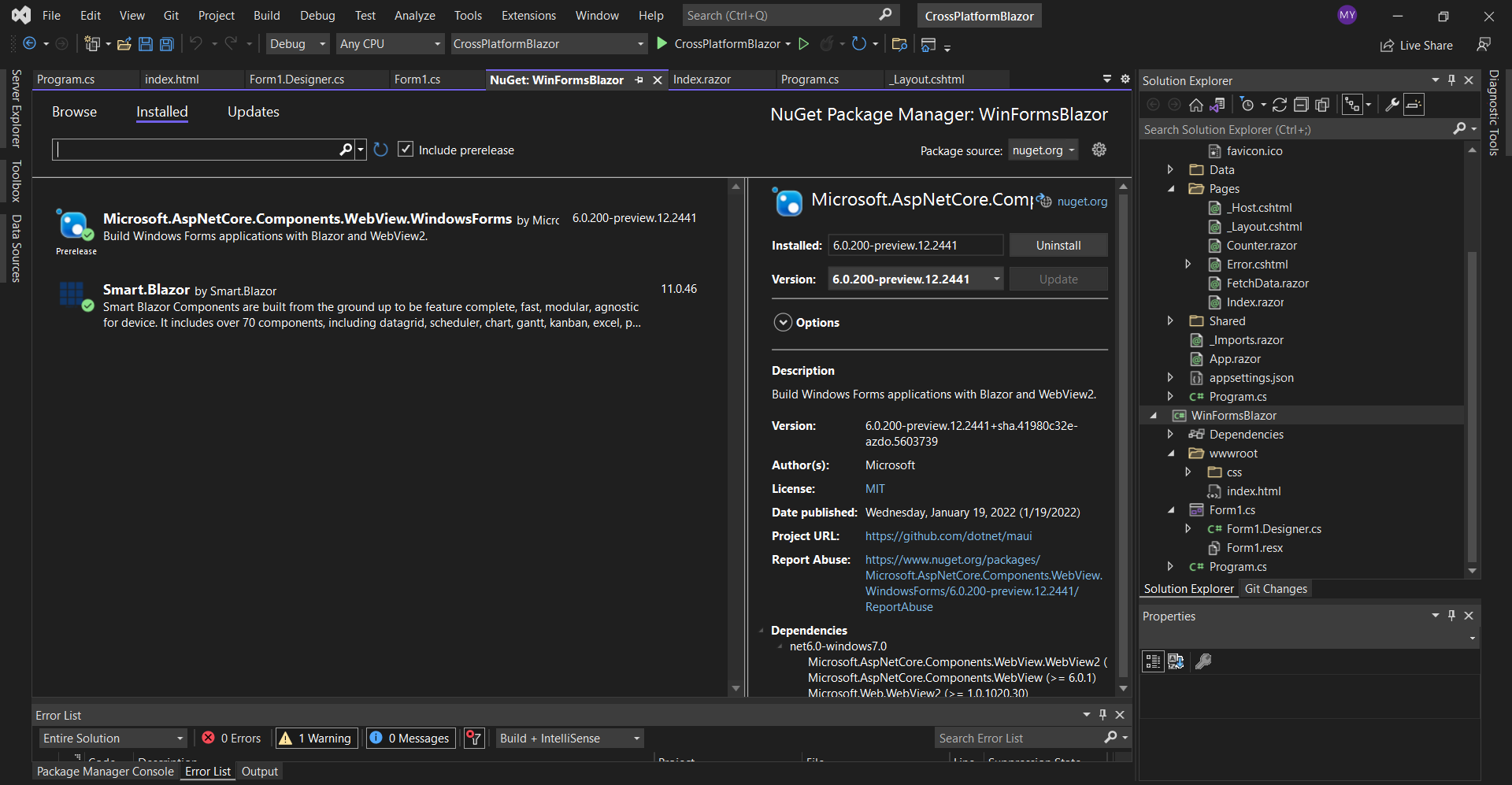
After that add a wwwroot folder which should contain an index.html file and a css folder.
You can copy the css folder from CrossPlatformBlazor project's wwwroot folder and the index.html file should look like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no" />
<title>Blazor WinForms app</title>
<base href="/" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap/bootstrap.min.css" />
<link href="css/site.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="WinFormsBlazor.styles.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="_content/Smart.Blazor/css/smart.default.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<div id="blazor-error-ui">
An unhandled error has occurred.
<a href="" class="reload">Reload</a>
<a class="dismiss">🗙</a>
</div>
<script src="_framework/blazor.webview.js"></script>
<script src="_content/Smart.Blazor/js/smart.blazor.js"></script>
<script src="_content/Smart.Blazor/js/smart.elements.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Blazor Class Library
We will extract the code shared between the Blazor Desktop app and the Blazor Server app in a separate Razor Class Library that we will call BlazorClassLibrary.
Again, add Smart.Blazor NuGet package to the project.
Then in the project file BlazorClassLibrary.csproj replace:
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
with
<AddRazorSupportForMvc>true</AddRazorSupportForMvc>
and add:
<ItemGroup>
<FrameworkReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.App" />
</ItemGroup>
Note, that you need to add a reference to the class library in the Blazor Server App and the Windows Forms App by right-clicking on them and choosing Add Project Refrence...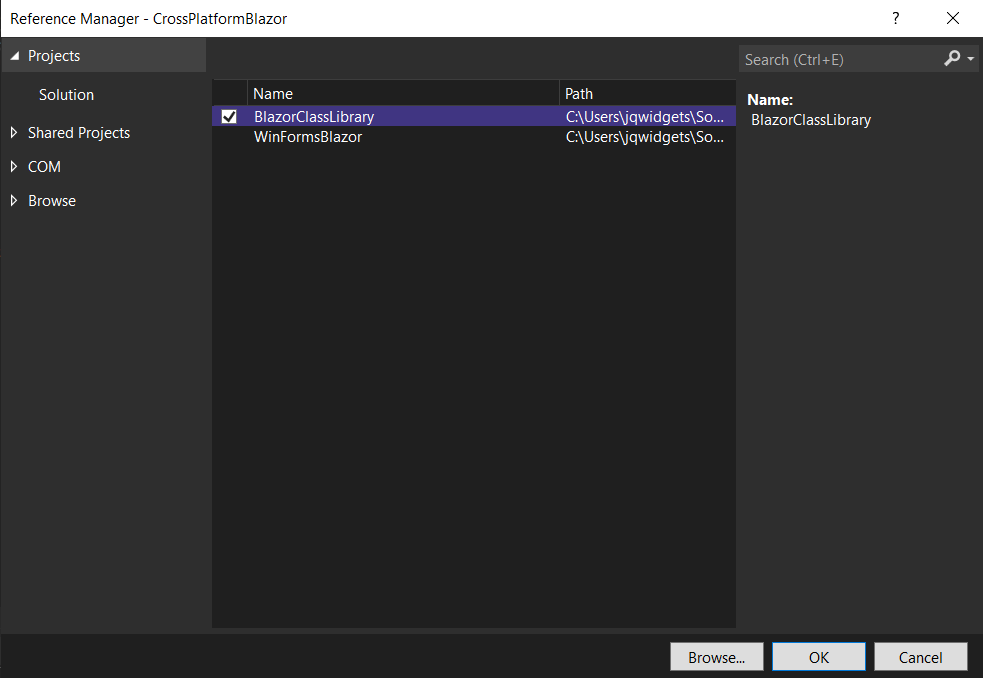
Now you can move
Data, Pages, Shared and wwwroot folders and _Imports.razor and App.Razor files from CrossPlatformBlazor to BlazorClassLibrary.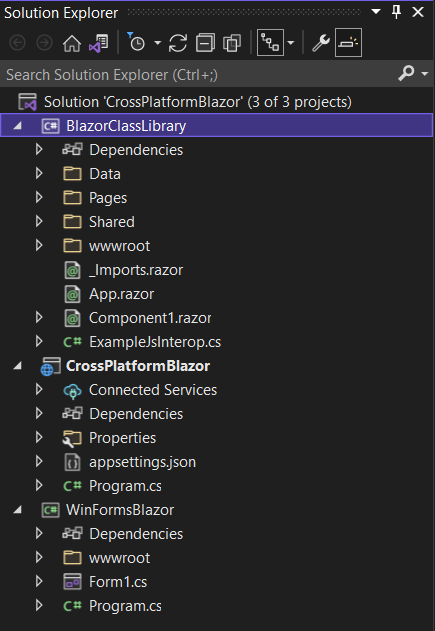
Then you should fix the reference of
ILogger inside \Pages\Error.cshtml.cs by adding:
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
Inside _Imports.razor replace:
@using CrossPlatformBlazor
@using CrossPlatformBlazor.Shared
with
@using BlazorClassLibrary
@using BlazorClassLibrary.Shared
Inside \Pages\_Layout.cshtml file you need to change the references of the css files by replacing:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap/bootstrap.min.css" />
<link href="css/site.css" rel="stylesheet" />
with
<link rel="stylesheet" href="_content/BlazorClassLibrary/css/bootstrap/bootstrap.min.css" />
<link href="_content/BlazorClassLibrary/css/site.css" rel="stylesheet" />
And finally, inside \Pages\_Host.cshtml add:
@using BlazorClassLibrary
Final Configurations
Lastly, in the WinFormsBlazor project you should open the Form1.cs file and paste this code:
using BlazorClassLibrary;
using CrossPlatformBlazor.Data;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Smart.Blazor;
namespace WinFormsBlazor
{
public partial class Form1 : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
public Form1()
{
var serviceCollection = new ServiceCollection();
serviceCollection.AddBlazorWebView();
serviceCollection.AddSingleton<WeatherForecastService>();
serviceCollection.AddSmart();
InitializeComponent();
blazorWebView1.HostPage = @"wwwroot\index.html";
blazorWebView1.Services = serviceCollection.BuildServiceProvider();
blazorWebView1.RootComponents.Add<App>("#app");
}
}
}
Then open also the Form1.Designer.cs file and paste the following code:
namespace WinFormsBlazor
{
partial class Form1
{
/// <summary>
/// Required designer variable.
/// </summary>
private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
/// <summary>
/// Clean up any resources being used.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing">true if managed resources should be disposed; otherwise, false.</param>
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing && (components != null))
{
components.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
/// <summary>
/// Required method for Designer support - do not modify
/// the contents of this method with the code editor.
/// </summary>
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.blazorWebView1 = new Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms.BlazorWebView();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// blazorWebView1
//
this.blazorWebView1.Anchor = ((System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles)((((System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles.Top | System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles.Bottom)
| System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles.Left)
| System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles.Right)));
this.blazorWebView1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(3, 7);
this.blazorWebView1.Name = "blazorWebView1";
this.blazorWebView1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(796, 436);
this.blazorWebView1.TabIndex = 20;
//
// Form1
//
this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(8F, 20F);
this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font;
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(800, 450);
this.Controls.Add(this.blazorWebView1);
this.Name = "Form1";
this.Text = "Form1";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
#endregion
private Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms.BlazorWebView blazorWebView1;
}
}
The last thing you need to do is to open the WinFormsBlazor's project file WinFormsBlazor.csproj and change the first line to:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Razor">
and add the following lines:
<ItemGroup>
<Content Update="wwwroot\**">
<CopyToOutputDirectory>PreserveNewest</CopyToOutputDirectory>
</Content>
</ItemGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<Content Update="wwwroot\css\site.css">
<CopyToOutputDirectory>PreserveNewest</CopyToOutputDirectory>
<ExcludeFromSingleFile>true</ExcludeFromSingleFile>
<CopyToPublishDirectory>PreserveNewest</CopyToPublishDirectory>
</Content>
</ItemGroup>
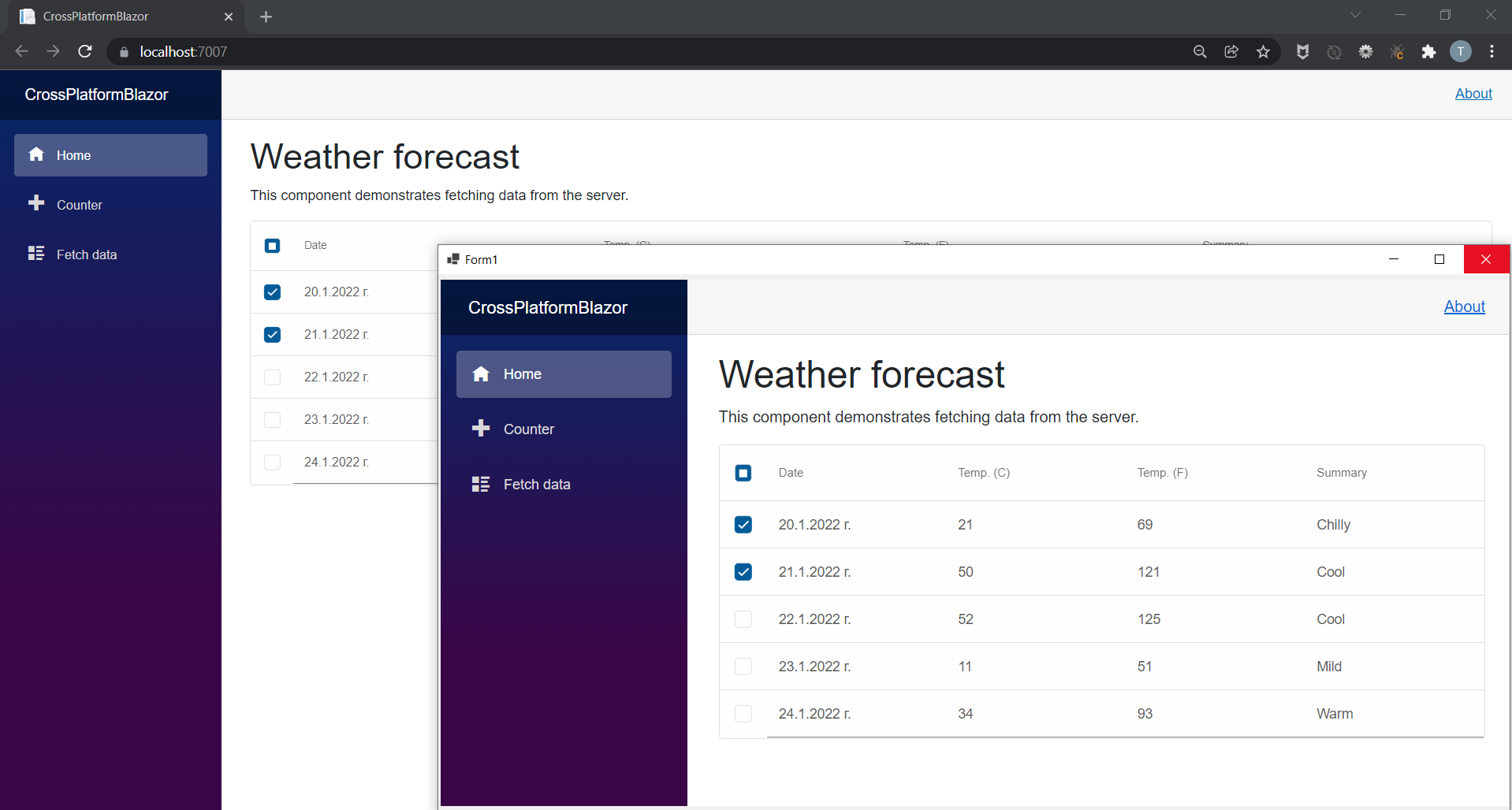
Now if you start both the CrossPlatformBlazor and WinFormsBlazor projects you should get the following result: