Build your web apps using Smart UI
Smart.Tabs - configuration and usage
Overview
Smart.Tabs element represents a custom element with selectable tabs and content sections associated with them.
Getting Started with Tabs Web Component
Smart UI for Web Components is distributed as smart-webcomponents NPM package. You can also get the full download from our website with all demos from the Download page.Setup the Tabs
Smart UI for Web Components is distributed as smart-webcomponents NPM package
- Download and install the package.
npm install smart-webcomponents
- Once installed, import the Tabs module in your application.
<script type="module" src="node_modules/smart-webcomponents/source/modules/smart.tabs.js"></script>
-
Adding CSS reference
The smart.default.css CSS file should be referenced using following code.
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="node_modules/smart-webcomponents/source/styles/smart.default.css" />
- Add the Tabs tag to your Web Page
<smart-tabs id="tabs"></smart-tabs>
- Create the Tabs Component
<script type="module"> Smart('#tabs', class { get properties() { return { selectedIndex: 0 } } }); </script>
Another option is to create the Tabs is by using the traditional Javascript way:
const tabs = document.createElement('smart-tabs'); tabs.disabled = true; document.body.appendChild(tabs);
Smart framework provides a way to dynamically create a web component on demand from a DIV tag which is used as a host. The following imports the web component's module and creates it on demand, when the document is ready. The #tabs is the ID of a DIV tag.
import "../../source/modules/smart.tabs.js"; document.readyState === 'complete' ? init() : window.onload = init; function init() { const tabs = new Smart.Tabs('#tabs', { selectedIndex: 0 }); }
- Open the page in your web server.
The following code adds the custom element to the page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../../source/styles/smart.default.css" type="text/css" />
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../source/smart.element.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../source/smart.tabs.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<smart-tabs>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 1" selected>
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 2">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 3">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
</smart-tabs>
</body>
</html>
Note how smart.element.js is declared before everything else. This is mandatory for all custom elements.
Demo

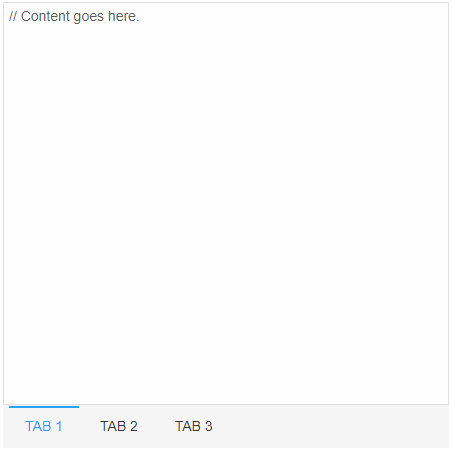
Appearance
The position of the tab strip is controlled by setting the property tabPosition. Possible values for it are:
- top
- bottom
- left
- right
- hidden
<smart-tabs tab-position="bottom">
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 1" selected>
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 2">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 3">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
</smart-tabs>
Demo
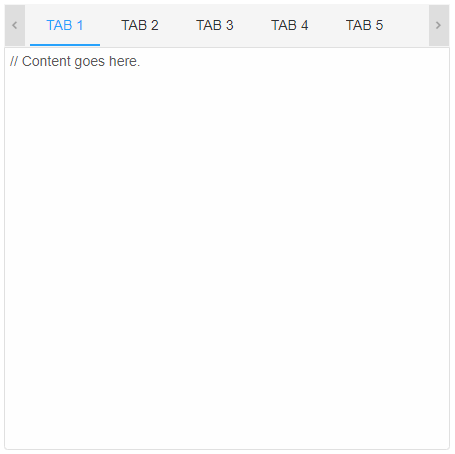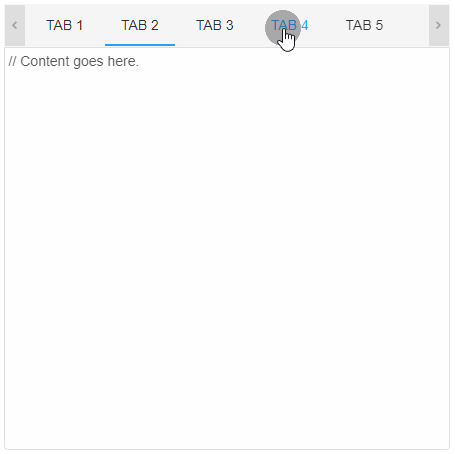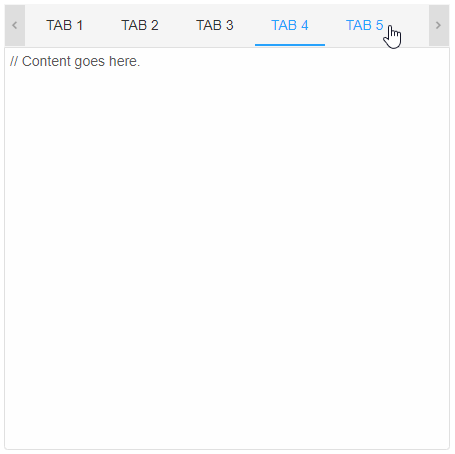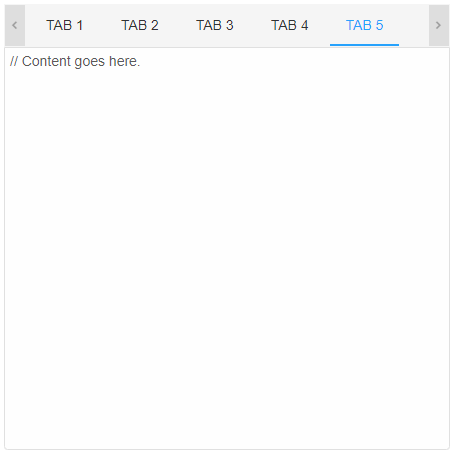
Behavior
When the custom element is not wide enough to display all tabs, one of four behaviours occurs. These are controlled by the overflow property and are:
- scroll - scroll buttons (instances of smart-repeat-button) allow the tabs to be scrolled through;
- dropdown - shows a dropdown with all tabs, even those that could not be displayed. Selecting an item from the dropdown makes its corresponding tab visible and selects it;
- wrap - all tabs are visible and are displayed on multiple lines (if necessary);
- shrink - tabs shrink in size (if necessary) so that all of them are visible on a single line (similar to how tabs behave in browsers).
<smart-tabs overflow="scroll">
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 1" selected>
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 2">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 3">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 4">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 5">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
</smart-tabs>
Demo
The initially selected tab is the one which has the attribute selected. Only one tab can be selected at a given time. If selected is not applied to any tab, the first one is selected by default. Selection can be dynamically changed using the mouse, keyboard and by calling the method select.
The property selectionMode determines the way the user can switch between tabs. Possible values are:
- click
- dblclick
- mouseenter
- none - tabs can be switched only programmatically.
<smart-tabs selection-mode="dblclick">
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 1" selected>
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 2">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
<smart-tab-item label="Tab 3">
// Content goes here.
</smart-tab-item>
</smart-tabs>
Demo
Tabs can be reordered by dragging with the mouse if the property reorder is set to true.
Content sections can be collapsed if the property collapsible is set to true and if the corresponding tab is clicked. Clicking the tab again restores the collapsed content section.
Keyboard Support
User can navigate between the tabs via arrow keys. Arrow Up and Arrow Left decreased the number of the selection, Arrow Down and Arrow Right increase it. Home moves the selection to the first tab, End to the last.
Create, Append, Remove, Get/Set Property, Invoke Method, Bind to Event
Create a new element:
const tabs = document.createElement('smart-tabs');
Append it to the DOM:
document.body.appendChild(tabs);
Remove it from the DOM:
tabs.parentNode.removeChild(tabs);
Set a property:
tabs.propertyName = propertyValue;
Get a property value:
const propertyValue = tabs.propertyName;
Invoke a method:
tabs.methodName(argument1, argument2);
Add Event Listener:
const eventHandler = (event) => {
// your code here.
};
tabs.addEventListener(eventName, eventHandler);
Remove Event Listener:
tabs.removeEventListener(eventName, eventHandler, true);
Using with Typescript
Smart Web Components package includes TypeScript definitions which enables strongly-typed access to the Smart UI Components and their configuration.
Inside the download package, the typescript directory contains .d.ts file for each web component and a smart.elements.d.ts typescript definitions file for all web components. Copy the typescript definitions file to your project and in your TypeScript file add a reference to smart.elements.d.ts
Read more about using Smart UI with Typescript.Getting Started with Angular Tabs Component
Setup Angular Environment
Angular provides the easiest way to set angular CLI projects using Angular CLI tool.
Install the CLI application globally to your machine.
npm install -g @angular/cli
Create a new Application
ng new smart-angular-tabs
Navigate to the created project folder
cd smart-angular-tabs
Setup the Tabs
Smart UI for Angular is distributed as smart-webcomponents-angular NPM package
- Download and install the package.
Quick Setup with ng-add
Smart Angular UI comes packaged with Angular CLI schematics to make creating Material applications easier. Schematics are included with both @angular/cdk and smart-webcomponents-angular. Once you install the npm packages, they will be available through the Angular CLI.Angular CLI supports the addition of packages through the ng add command. The ng add command provides faster and more user-friendly package installation. To install the Smart UI for Angular package use ng add and add the name of the NPM package.
ng add smart-webcomponents-angular
The ng add smart-webcomponents-angular command executes the following actions:
- Adds the smart-webcomponents-angular package as a dependency.
- Imports the Modules in the current application module.
- Registers the default Smart UI theme in the angular.json file.
- Adds all required peer dependencies to package.json.
- Triggers npm install to install the theme and all peer packages that are added.
Manual Setup
npm install smart-webcomponents-angular
- Adding CSS reference
The following CSS file is available in ../node_modules/smart-webcomponents-angular/ package folder. This can be referenced in [src/styles.css] using following code.@import 'smart-webcomponents-angular/source/styles/smart.default.css';
Another way to achieve the same is to edit the angular.json file and in the styles add the style."styles": [ "node_modules/smart-webcomponents-angular/source/styles/smart.default.css" ]
If you want to use Bootstrap, Fluent or other themes available in the package, you need to add them after 'smart.default.css'. -
Example with Angular Standalone Components
app.component.html
<smart-tabs #tabs class="demoTabs" [selectedIndex]="1"> <smart-tab-item [label]="'TAB 1'">Content 1</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item [label]="'TAB 2'">Content 2</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item [label]="'TAB 3'">Content 3</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item [label]="'TAB 4'">Content 4</smart-tab-item> </smart-tabs>
app.component.ts
import { Component, ViewChild, OnInit, AfterViewInit } from '@angular/core'; import { TabsComponent } from 'smart-webcomponents-angular/tabs'; import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common'; import { RouterOutlet } from '@angular/router'; import { TabsModule } from 'smart-webcomponents-angular/tabs'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', standalone: true, imports: [CommonModule, TabsModule, RouterOutlet], templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'] }) export class AppComponent implements AfterViewInit, OnInit { @ViewChild('tabs', { read: TabsComponent, static: false }) tabs!: TabsComponent; ngOnInit(): void { // onInit code. } ngAfterViewInit(): void { // afterViewInit code. this.init(); } init(): void { // init code. } }
-
Example with Angular NGModule
app.component.html
<smart-tabs #tabs class="demoTabs" [selectedIndex]="1"> <smart-tab-item [label]="'TAB 1'">Content 1</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item [label]="'TAB 2'">Content 2</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item [label]="'TAB 3'">Content 3</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item [label]="'TAB 4'">Content 4</smart-tab-item> </smart-tabs>
app.component.ts
import { Component, ViewChild, OnInit, AfterViewInit } from '@angular/core'; import { TabsComponent } from 'smart-webcomponents-angular/tabs'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'] }) export class AppComponent implements AfterViewInit, OnInit { @ViewChild('tabs', { read: TabsComponent, static: false }) tabs!: TabsComponent; ngOnInit(): void { // onInit code. } ngAfterViewInit(): void { // afterViewInit code. this.init(); } init(): void { // init code. } }
app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { TabsModule } from 'smart-webcomponents-angular/tabs'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule, TabsModule ], bootstrap: [ AppComponent ] }) export class AppModule { }
Running the Angular application
After completing the steps required to render a Tabs, run the following command to display the output in your web browser
ng serveand open localhost:4200 in your favorite web browser.
Read more about using Smart UI for Angular: https://www.htmlelements.com/docs/angular-cli/.
Getting Started with React Tabs Component
Setup React Environment
The easiest way to start with React is to use NextJS Next.js is a full-stack React framework. It’s versatile and lets you create React apps of any size—from a mostly static blog to a complex dynamic application.
npx create-next-app my-app cd my-app npm run devor
yarn create next-app my-app cd my-app yarn run dev
Preparation
Setup the Tabs
Smart UI for React is distributed as smart-webcomponents-react package
- Download and install the package.
In your React Next.js project, run one of the following commands to install Smart UI Tabs for ReactWith NPM:
npm install smart-webcomponents-react
With Yarn:yarn add smart-webcomponents-react
- Once installed, import the React Tabs Component and CSS files in your application and render it.
app.js
import 'smart-webcomponents-react/source/styles/smart.default.css'; import React from "react"; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; import { Tabs, TabItem, TabItemsGroup } from 'smart-webcomponents-react/tabs'; const App = () => { return ( <div> <Tabs selectedIndex={1}> <TabItem label="TAB 1">Content 1</TabItem> <TabItem label="TAB 2">Content 2</TabItem> <TabItem label="TAB 3">Content 3</TabItem> <TabItem label="TAB 4">Content 4</TabItem> </Tabs> </div> ); } export default App;
Running the React application
Start the app withnpm run devor
yarn run devand open localhost:3000 in your favorite web browser to see the output.
Setup with Vite
Vite (French word for "quick", pronounced /vit/, like "veet") is a build tool that aims to provide a faster and leaner development experience for modern web projectsWith NPM:
npm create vite@latestWith Yarn:
yarn create viteThen follow the prompts and choose React as a project.
Navigate to your project's directory. By default it is 'vite-project' and install Smart UI for React
In your Vite project, run one of the following commands to install Smart UI Tabs for ReactWith NPM:
npm install smart-webcomponents-reactWith Yarn:
yarn add smart-webcomponents-reactOpen src/App.tsx App.tsx
import 'smart-webcomponents-react/source/styles/smart.default.css';
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import { Tabs, TabItem, TabItemsGroup } from 'smart-webcomponents-react/tabs';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<Tabs selectedIndex={1}>
<TabItem label="TAB 1">Content 1</TabItem>
<TabItem label="TAB 2">Content 2</TabItem>
<TabItem label="TAB 3">Content 3</TabItem>
<TabItem label="TAB 4">Content 4</TabItem>
</Tabs>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Read more about using Smart UI for React: https://www.htmlelements.com/docs/react/.
Getting Started with Vue Tabs Component
Setup Vue with Vite
In this section we will introduce how to scaffold a Vue Single Page Application on your local machine. The created project will be using a build setup based on Vite and allow us to use Vue Single-File Components (SFCs). Run the following command in your command linenpm create vue@latestThis command will install and execute create-vue, the official Vue project scaffolding tool. You will be presented with prompts for several optional features such as TypeScript and testing support:
✔ Project name: …If you are unsure about an option, simply choose No by hitting enter for now. Once the project is created, follow the instructions to install dependencies and start the dev server:✔ Add TypeScript? … No / Yes ✔ Add JSX Support? … No / Yes ✔ Add Vue Router for Single Page Application development? … No / Yes ✔ Add Pinia for state management? … No / Yes ✔ Add Vitest for Unit testing? … No / Yes ✔ Add an End-to-End Testing Solution? … No / Cypress / Playwright ✔ Add ESLint for code quality? … No / Yes ✔ Add Prettier for code formatting? … No / Yes Scaffolding project in ./ ... Done.
cdnpm install npm install smart-webcomponents npm run dev
-
Make Vue ignore custom elements defined outside of Vue (e.g., using the Web Components APIs). Otherwise, it will throw a warning about an Unknown custom element, assuming that you forgot to register a global component or misspelled a component name.
Open vite.config.js in your favorite text editor and change its contents to the following:
vite.config.js
import { fileURLToPath, URL } from 'node:url' import { defineConfig } from 'vite' import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue' // https://vitejs.dev/config/ export default defineConfig({ plugins: [ vue({ template: { compilerOptions: { isCustomElement: tag => tag.startsWith('smart-') } } }) ], resolve: { alias: { '@': fileURLToPath(new URL('./src', import.meta.url)) } } }) -
Open src/App.vue in your favorite text editor and change its contents to the following:
App.vue
<template> <div class="vue-root"> <div id="tabs"></div> </div> </template> <script> import { onMounted } from "vue"; import "smart-webcomponents/source/styles/smart.default.css"; import "smart-webcomponents/source/modules/smart.tabs.js"; export default { name: "app", setup() { onMounted(() => { window.tabs.innerHTML = ` <smart-tabs class="demoTabs" selected-index="1"> <smart-tab-item label="TAB 1">Content 1</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item label="TAB 2">Content 2</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item label="TAB 3">Content 3</smart-tab-item> <smart-tab-item label="TAB 4">Content 4</smart-tab-item> </smart-tabs> `; }); } }; </script> <style> </style>We can now use the smart-tabs with Vue 3. Data binding and event handlers will just work right out of the box.
Running the Vue application
Start the app withnpm run devand open http://localhost:5173/ in your favorite web browser to see the output below:
When you are ready to ship your app to production, run the following:
npm run buildThis will create a production-ready build of your app in the project's ./dist directory.
Read more about using Smart UI for Vue: https://www.htmlelements.com/docs/vue/.